Couplings, Torque Arms and
Hold Backs
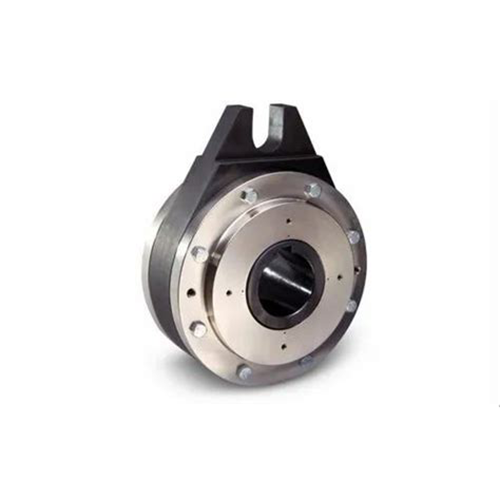
Couplings
Couplings are essential components in industrial machines, especially when gears are involved. They play a crucial role in connecting two rotating shafts, allowing for the transmission of mechanical power, torque, and motion from one shaft to another. Couplings are versatile and come in various types, each suited to specific applications. Here’s an overview of couplings and their significance in industrial machinery, particularly in conjunction with gears:
1. Transmitting Torque: One of the primary functions of couplings is to transmit torque between two shafts. When gears are used in a machine, couplings ensure that the torque generated by one gear is effectively transferred to the next gear or component.
2. Compensation for Misalignment: Shafts in industrial machines may not always be perfectly aligned due to manufacturing tolerances or operating conditions. Flexible couplings can accommodate these misalignments by flexing or allowing slight angular and axial movement while maintaining the torque transmission.
3. Reducing Vibration and Shock: Couplings can help dampen vibrations and reduce shock loads between connected components. This is especially important when gears are involved, as smooth, controlled motion is critical for gear efficiency and longevity.
4. Electrical Isolation: In some cases, couplings are used to electrically isolate shafts. This is crucial in machines where electrical interference or grounding issues need to be prevented, such as in sensitive electronic equipment.
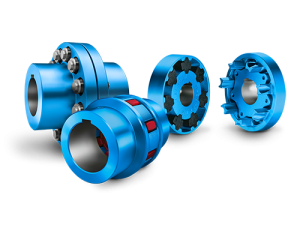
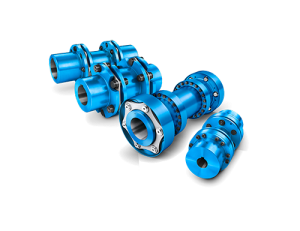
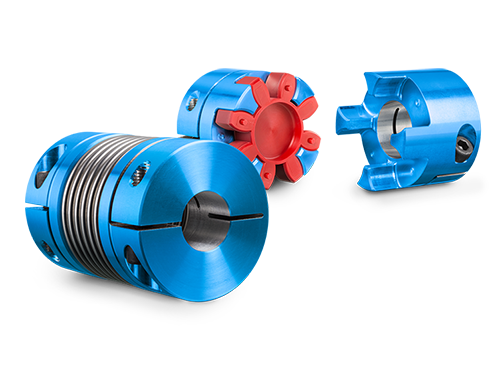
5. Types of Couplings: There are several types of couplings, including:
Rigid Couplings: These provide a solid connection between two shafts, ideal for applications where misalignment is minimal.
Flexible Couplings: Designed to compensate for shaft misalignment, these couplings include elastomeric (rubber), jaw, and bellows types.
Gear Couplings: These are specifically designed for connecting two gear shafts. They provide high torque capacity and are suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Chain Couplings: Consisting of interconnected chains, these couplings are used in applications that require shock absorption and misalignment compensation.
Universal Joints (U-Joints): U-joints allow for angular misalignment and are often used in vehicles and machinery that require a connection between non-collinear shafts.
6. Maintenance and Lubrication: Depending on the type of coupling, regular maintenance and lubrication may be necessary to ensure proper functioning and to extend the coupling’s lifespan. Neglecting maintenance can lead to premature wear and failure.
Couplings are indispensable in industrial machines, particularly when gears are involved. They facilitate the smooth transmission of torque, compensate for misalignment, reduce vibration, and ensure the efficient operation of machinery. Selecting the right type of coupling for a specific application is critical to achieving optimal performance and longevity in industrial systems.


Holdbacks
Holdbacks, also known as backstops or clutches, are mechanical components commonly used in industrial machines and equipment to prevent unintended reverse motion or backdriving of a system. They serve as a safety feature and are crucial in situations where it is essential to maintain control over the direction of movement, particularly in conveyors, elevators, and other machinery where gravity or external forces may cause reverse motion.
Here are some key features and functions of holdbacks in industrial machines:
Preventing Reverse Motion: The primary purpose of a holdback is to prevent machinery from moving in the reverse direction when the primary driving force is removed or reduced. This is particularly important in applications like conveyor systems, where materials need to be transported in one direction only.
Safety and Control: Holdbacks enhance safety by maintaining control over equipment and preventing uncontrolled or unintended movement. In situations where a sudden reversal could pose a hazard to workers or damage to equipment, holdbacks act as a critical safety feature.
Types of Holdbacks: Holdbacks come in various designs, including mechanical, electrical, and hydraulic types. Mechanical holdbacks often use ratcheting mechanisms or clutches to engage and disengage, while electrical and hydraulic holdbacks use solenoids or valves for control.
Backstop Function: In the context of conveyor systems, holdbacks are often referred to as “backstops.” A backstop ensures that the conveyor belt cannot move backward when it is not actively driven. This is especially important when conveying heavy or bulk materials on an incline.
Overrunning Protection: Holdbacks are also used in machinery that needs protection from overrunning or backdriving. For instance, in a winch or hoist system, a holdback can prevent the load from lowering uncontrollably when the winch is not actively powered.
Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of holdbacks are crucial to ensure their proper functioning. This includes checking for wear and tear, lubrication, and verifying that the holdback engages and disengages as expected.
Variety of Applications: Holdbacks are employed in a wide range of industrial applications, including conveyor systems, cranes, hoists, mining equipment, and many others where controlling the direction of motion is critical for safety and operational efficiency.
Holdbacks are essential components in industrial machinery and equipment, helping to maintain control over the direction of motion, enhance safety, and prevent unintended reverse movement. They play a pivotal role in ensuring the efficient and safe operation of various industrial systems.




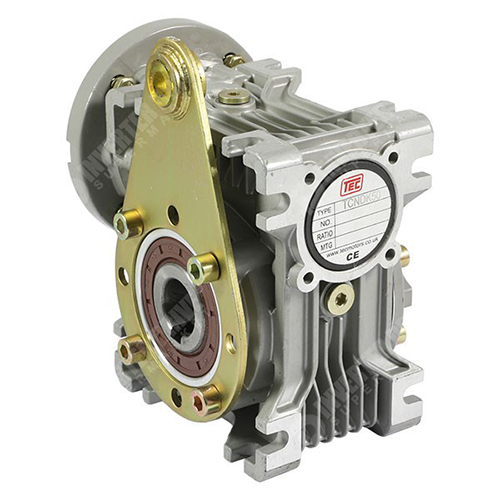
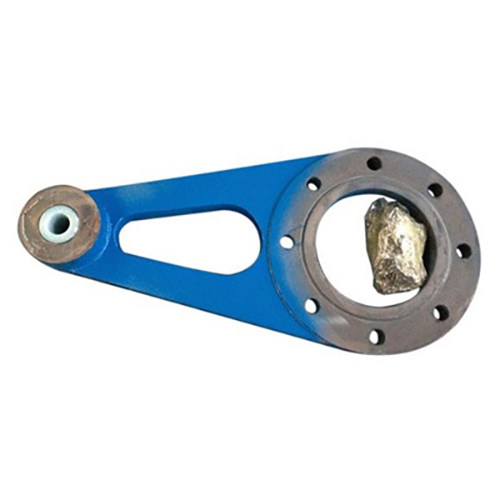
Torque Arms
Torque arms are mechanical devices or components used in various engineering and industrial applications to control, support, or manage the torque (rotational force) generated by a rotating object or machinery. They are designed to provide stability, reduce vibration, and prevent excessive movement or misalignment in systems where torque is a critical factor.
Here are some key aspects of torque arms:
Support and Stabilization: Torque arms are often used to support and stabilize heavy equipment or rotating machinery, such as electric motors, engines, pumps, or industrial robots. They help prevent excessive movement or vibration that could lead to wear and tear, misalignment, or even structural damage.
Alignment: In many applications, precise alignment of rotating components is crucial for efficient operation and longevity. Torque arms can be used to maintain the correct alignment of shafts, couplings, or other rotating parts, ensuring that they stay properly connected and don’t experience undue stress.
Load Distribution: Torque arms distribute the torque load generated by a rotating component to a fixed or anchored point, which helps in balancing the forces involved. This can prevent overloading and extend the lifespan of both the machinery and its supporting structures.
Vibration Dampening: Excessive vibration can be harmful to both equipment and the surrounding environment. Torque arms can dampen vibrations by providing a stable connection and reducing the transmission of vibrations to other parts of the system.
Adjustability: Many torque arms are designed with adjustable features, allowing engineers and operators to fine-tune the torque support based on specific requirements. This adjustability makes them versatile and adaptable to different applications.
Safety: Torque arms contribute to safety in industrial settings by preventing unexpected movements or shifts in machinery that could lead to accidents or damage. They are often used in combination with safety measures and mechanisms.
Industrial and Automotive Applications: Torque arms find applications in a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, automotive assembly lines, conveyor systems, and any situation where precise control of torque is necessary.
Torque arms play a critical role in various industrial and mechanical systems by providing support, stability, and control over torque, ultimately helping to enhance efficiency, safety, and the longevity of equipment and machinery.


Contact Us
Office Address:
29 Arnold Ave
Bardene
Boksburg
Contact Telephone: +27 84 679 4566
Emails:
Accounts: accounts@jclminingsupplies.co.za
Sales: sales@jclminingsupplies.co.za
Business Hours:
8:00-16:30 Monday – Thursday
8:00-13:00 Friday
